The magnetism of mid ocean ridges helped scientists first identify the process of seafloor spreading in the early 20th century.
The process of seafloor spreading does not produce new seafloor.
The red sea has not yet completely split arabia from africa but a similar feature can be found on the other side of africa that has broken completely free.
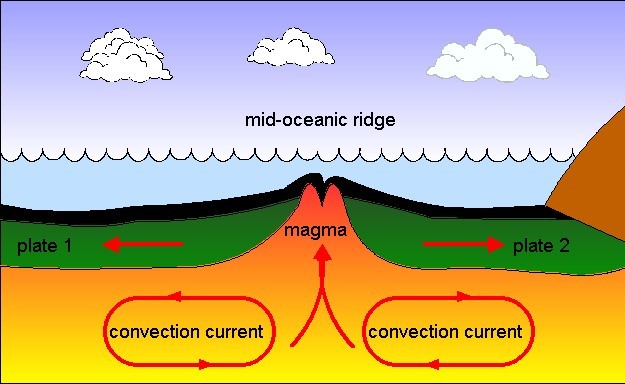
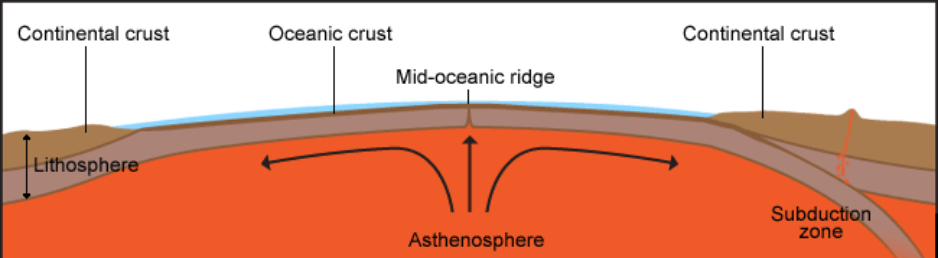
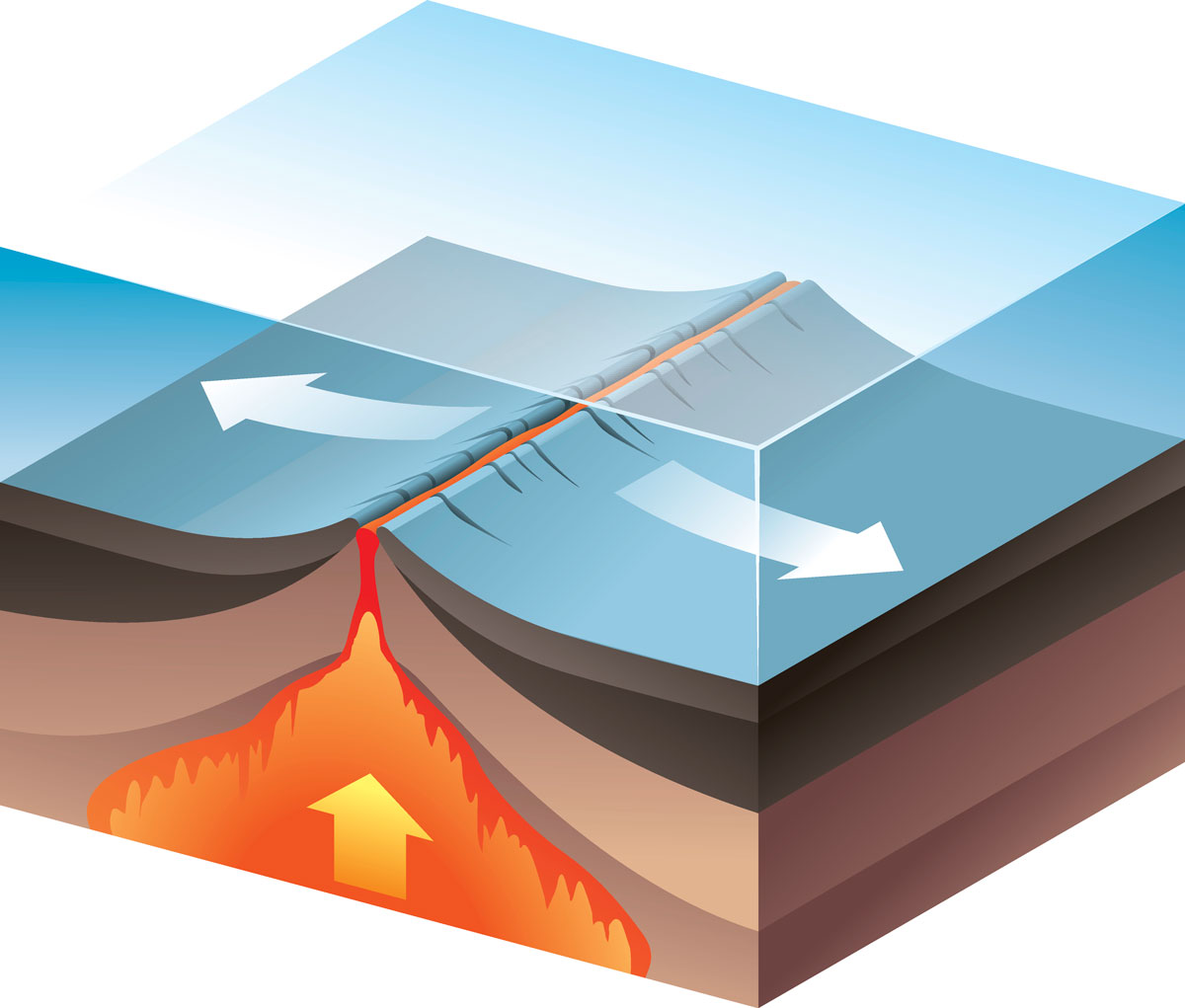
Seafloor spreading theory that oceanic crust forms along submarine mountain zones and spreads out laterally away from them.
The mid ocean ridge is the region where new oceanic crust is created.
Basalt the once molten rock that makes up most new oceanic crust is a fairly magnetic substance and scientists began using magnetometers to measure the magnetism of the ocean floor in the 1950s what they discovered was that the magnetism of the ocean floor around.
The oceanic crust is composed of rocks that move away from the ridge as new crust is being formed.
These age data also allow the rate of seafloor spreading to be determined and they show that rates.
The process of sea floor spreading.
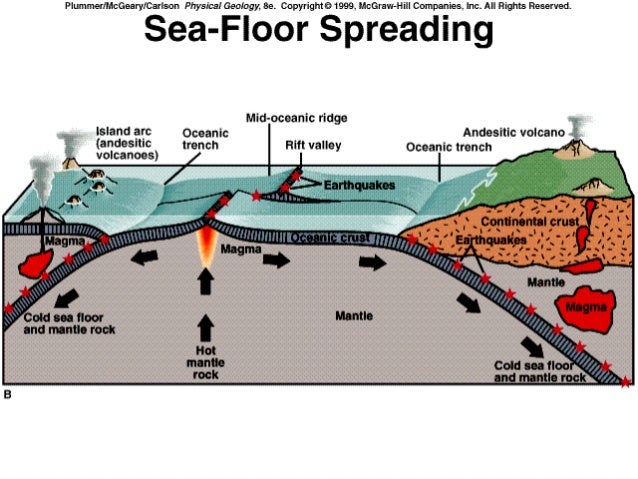
The process of seafloor spreading leads to the formation of numerous geographical features which can be terrestrial sub terrestrial or marine features.
Seafloor spreading is credited for the formation of the red sea as a result of the movement of the arabian and african tectonic plates away from each other.
This idea played a pivotal role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics which revolutionized geologic thought during the last quarter of the 20th century.
As upwelling of magma continues the plates continue to diverge a process known as seafloor spreading samples collected from the ocean floor show that the age of oceanic crust increases with distance from the spreading centre important evidence in favour of this process.
Strong evidence of seafloor spreading and plate tectonics.
Paleomagnetism led the revival of the continental drift hypothesis and its transformation into theories of sea floor spreading and plate tectonics.